Understanding the Pareto principle
When you start your day, what’s the first thing you do? Most of us grab our caffeinated beverage of choice, check email, and prioritize tasks for the day. How do we identify what needs to get done first?
One common technique is called the Pareto principle, also known as the 80/20 rule. This technique can help determine and prioritize the highest-impact tasks, thereby increasing productivity throughout the day.
What is the Pareto principle?
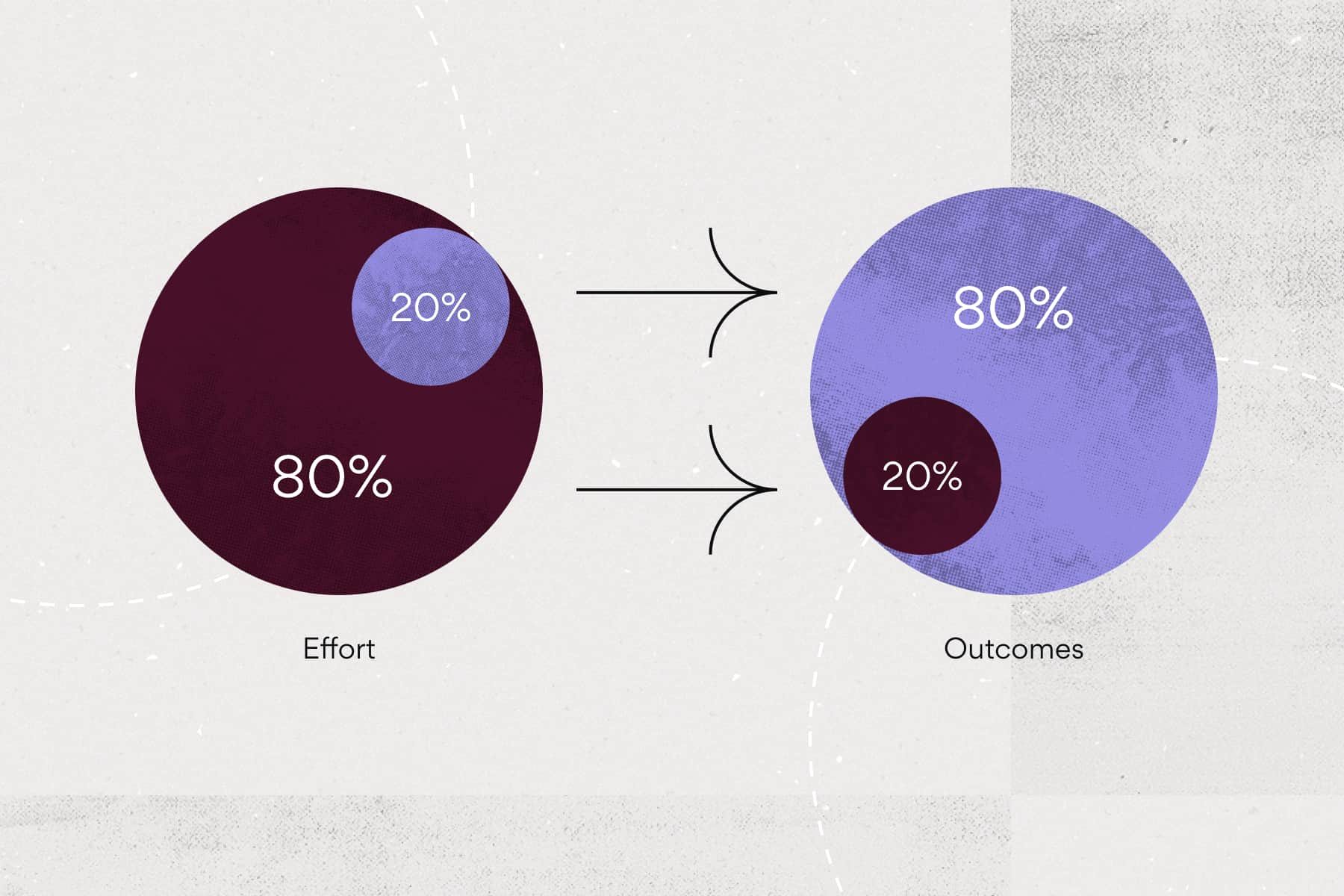
The Pareto principle states that for many outcomes, roughly 80% of consequences come from 20% of causes. A small percentage of causes have an outsized effect. This concept is important to understand because it can help identify which initiatives to prioritize for the most impact.
Where does the Pareto principle come from?
This phenomenon also goes by a couple of different names:
- Pareto principle
- The 80/20 rule (most common)
The 80/20 rule is not a formal mathematical equation. It is a rule of thumb, not a law of nature. It’s observed in economics, business, time management, and even sports.
General examples of the Pareto principle:
- 20% of a plant contains 80% of the fruit
- 80% of a company’s profits come from 20% of customers
- 20% of players result in 80% of points scored
How to use the 80/20 rule
The 80/20 rule applies to almost every industry. The Pareto principle is commonly used in business and economics. This is because the 80/20 rule is helpful in determining where to focus efforts towards maximizing output.
The basis of the Pareto principle states that 80% of results come from 20% of actions. Work that can be segmented into smaller parts allows the Pareto principle to help identify what part of that work is the most influential.
Here are a few examples of how to use the tool in practice.
Productivity
Use the 80/20 rule to prioritize the tasks needing to get done during the day.
Out of the entire task list, completing 20% of those tasks will result in 80% of the impact on that day. So, in order to get the most accomplished, identify which tasks have the most impact and focus on those for the day.
Decision making
The Pareto principle can help you to make the best decisions during the problem-solving process. When there are many causes to one problem, the Pareto principle can help prioritize solutions. Here are a few steps to how this works:
- Identify the problems within this decision-making process.
- Identify the causes of these problems.
- Categorize problems into similar groups. This can help determine if one solution can resolve multiple issues.
- Assign a value to each of these problems based on its impact on the project. The value can be as simple as a number between 1-10, or actual monetary value to show the importance.
- Develop a plan to focus on the top 20% of the problems that impact the project. One solution can resolve multiple problems. Based on the values assigned to each problem, calculate which ones are in the top 20%. Once you’ve identified the main problem, develop a plan to create a solution that can cause 80% of the results using problem-solving strategies.
Example of how to use the 80/20 rule for decision making:
Imagine an ecommerce company. 100 of the most recent customer service complaints come from the fact that customers are receiving damaged products. 80% of refunds given were for damaged products.
Improving packaging to protect products during shipping resolves the issue with customers receiving damaged products.
Quality control
The Pareto analysis and the Pareto chart are key tools used within the Six Sigma quality control methodology.
In the Six Sigma methodology, using a Pareto chart can help visualize your data to identify how to prioritize actions. Six Sigma’s main goal is to reduce the amount of variation in a process with the goal of increasing the amount of production. Pareto charts are common in Six Sigma methodology because they help to identify what most of the variations are in a process.
Advantages of using the Pareto principle
The biggest advantage of using the Pareto principle is to create the maximum amount of impact with the least amount of work. This facilitates the best use of time, focus, and resources.
The 80/20 rule improves metrics by prioritizing initiatives in the right order.
Other benefits of using the Pareto principle:
- Clear priorities
- Increased daily productivity
- Ability to portion work into manageable segments
- More focused strategy

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.